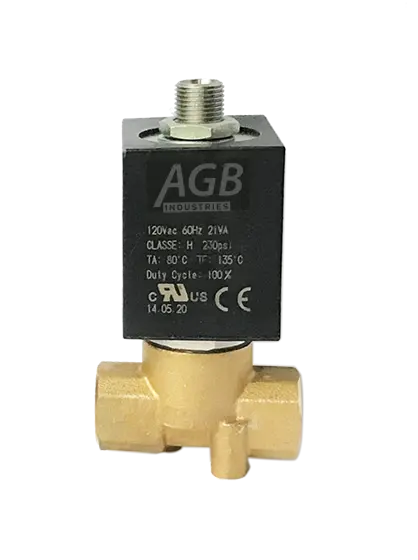
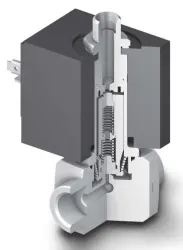
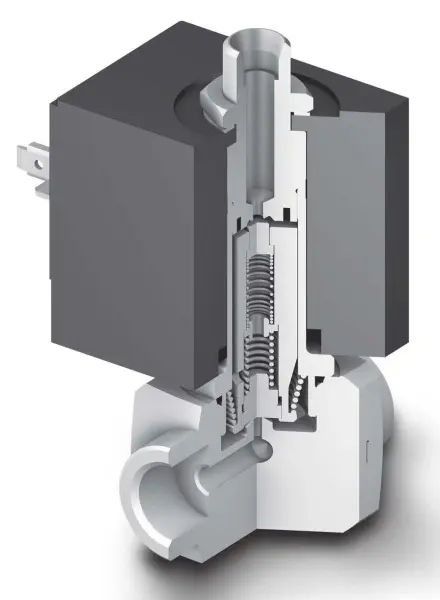
3 Way Normally Closed Solenoid Valves
3 Way Solenoid Valve Features
- No minimum pressure required
- Mountable in any position
- Wide variety of seal material options
3 Way Solenoid Valves
This indicates that the valve has three ports: typically, one inlet, one normally closed outlet, and one alternative outlet. 3 way solenoid valves are used for applications where fluid flow can be directed between two different pathways.
Normally Closed Solenoid Valves
The "normally closed" designation means that the solenoid valve is closed (blocking flow) in its default state when not energized. In other words, when the valve is at rest and there is no electrical current applied to the solenoid coil, the flow of fluid is blocked. It only opens when the solenoid is energized.
Alternative Outlet
In a 3-way normally closed solenoid valve, when the solenoid is energized, it redirects the flow of fluid from the normally closed outlet to an alternative outlet. This change in flow path allows the fluid to be directed to a different location or component within the system.
These 3-way normally closed solenoid valves are used in various applications where fluid flow needs to be redirected or controlled between two different routes or where a default closed position is required for safety or system integrity. Common applications include pneumatic systems, hydraulic systems, and industrial automation where switching between two functions is necessary.